Aside from the size and orientation of the house itself, the major factors that go into the baseline model are Climate, Insulation, Air Infiltration and Windows.

Climate, of course, plays a major factor in the design of an energy efficient home. An approach that's appropriate for a cold climate may not work for a hot climate.
North Georgia is in the southern edge of IECC 2009 Climate Zone 4.
The station has established an average of 4147 Heating Degree Days (HDD) and an average of 857 Cooling Degree Days (CDD) over the past ten years.
For a passive solar design it's also important to have an estimate of the solar energy available at your site. The National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL) publishes detailed solar data for all 50 states here http://rredc.nrel.gov/solar/pubs/redbook/ and has a dynamic map visualization site here http://www.nrel.gov/gis/
The DOE recommended insulation levels for Zone 4 are:
- Attic or Ceiling R38
- Walls R21
- Floor over unheated space R25
- Slab R5
Georgia code requires a maximum ACH50 score of 7 air changes per hour (not very good).
There is some confusion on the allowable characteristics for windows. The prescriptive window requirements in the 2009 IECC specify U of 0.35 for Climate Zone 4 and place no restriction on SHGC for Climate Zone 4.
See the Efficient Windows Collaborative link here http://www.efficientwindows.org/code_overview.cfm
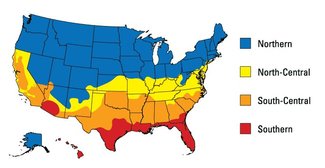
The table lists the Energy Star maximum U-Factor and maximum SHGC allowed for each region.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed